You are interested in Data Privacy in Cybersecurity: Protecting Your Information right? So let's go together qule.info look forward to seeing this article right here!
In the digital age, where technology has become an integral part of our lives, the importance of data privacy in cybersecurity cannot be overstated. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, safeguarding our personal and confidential information has become a critical concern. In this article, Qule.info will delve into data privacy in cyber security realm of data privacy in cyber security, exploring its significance, key challenges, and strategies to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
Data Privacy in Cyber security: Protecting Your Information
- Understanding Data Privacy and Cybersecurity:
Data privacy refers to the protection of personal information, ensuring that it is collected, stored, and used in a manner that respects individuals’ rights and maintains their confidentiality. Cybersecurity, on the other hand, encompasses measures and practices designed to safeguard computer systems, networks, and data from cyber threats, such as data privacy in cyber security, malware, and identity theft. The intersection of data privacy and cybersecurity is crucial for maintaining the trust and security of individuals and organizations in the digital landscape. - The Significance of Data Privacy in Cybersecurity:
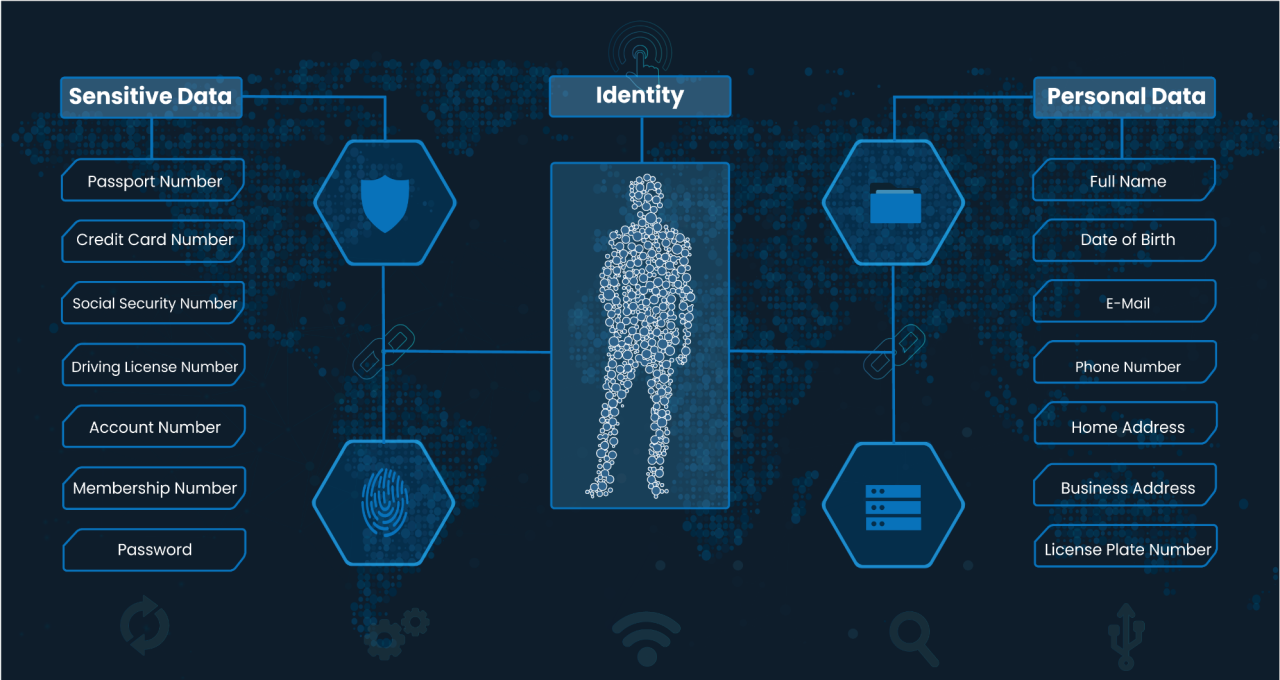
Data privacy plays a pivotal role in cybersecurity by safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access. Personal data privacy in cyber security, including names, addresses, social security numbers, and financial details, are valuable assets for cybercriminals. By compromising data privacy, cybercriminals can exploit individuals’ identities, commit financial fraud, or engage in other malicious activities. Protecting data privacy is not only essential for individuals but also for businesses, as data breaches can result in severe financial and reputational damage. - Key Challenges in Data Privacy:
Ensuring data privacy in cyber security comes with its own set of challenges. Rapid technological advancements, evolving cyber threats, and complex data ecosystems make it increasingly difficult to protect sensitive information. Additionally, the collection and use of personal data by various entities, such as social media platforms and online service providers, raise concerns about how data is handled, shared, and secured. Balancing data privacy rights with technological innovation and business needs requires careful consideration and effective strategies. - Legal and Regulatory Frameworks:
To address the challenges associated with data privacy in cyber security, governments and regulatory bodies have implemented legal frameworks and regulations. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets stringent requirements for organizations handling personal data, including consent, data minimization, and the right to erasure. Similarly, other countries and regions have enacted laws to protect data privacy, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and individual rights. Compliance with these regulations is crucial for organizations to build trust with their customers and avoid legal repercussions. - Privacy by Design: Building Data Privacy into Cybersecurity:
Privacy by Design (PbD) is a proactive approach that integrates data privacy in cyber security measures into the design and development of systems, processes, and technologies. By considering data privacy from the outset, organizations can minimize risks and enhance the security of personal information. PbD emphasizes principles such as data minimization, purpose limitation, and user-centric design, ensuring that privacy is embedded into every aspect of an organization’s operations.
- Encryption and Anonymization:
Encryption and anonymization techniques play a vital role in protecting data privacy in cyber security. Encryption involves converting data into an unreadable format, which can only be deciphered with a decryption key. This ensures that even if unauthorized persons gain access to the data, they cannot interpret it without the encryption key. Anonymization, on the other hand, removes or modifies identifying information from datasets, making it difficult to link the data to specific individuals. By employing these techniques, organizations can add an extra layer of protection to sensitive data. - Secure Data Storage and Transmission:
Securing data storage and transmission is essential to maintaining data privacy in cyber security. Organizations should implement robust security measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access controls, to safeguard data stored in databases and servers. Furthermore, secure transmission protocols, such as HTTPS and VPNs, should be used to encrypt data while it is being transmitted over networks. By adopting these measures, organizations can mitigate the risk of unauthorized access and interception of sensitive information. - Employee Education and Awareness:
Data privacy in cybersecurity is not solely dependent on technological measures; it also relies on the awareness and actions of individuals. Organizations should prioritize employee education and training programs to promote a culture of data privacy. Employees should be educated about the significance of data privacy, the potential risks, and best practices for protecting sensitive information. By fostering a privacy-conscious workforce, organizations can minimize human errors and enhance overall data security. - Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response:
Data privacy is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and proactive incident response. Organizations should implement robust monitoring systems to detect any unauthorized access attempts, suspicious activities, or data breaches. In the event of a security incident, a well-defined incident response plan should be in place to minimize the impact, investigate the breach, and notify affected individuals or authorities promptly. Timely and transparent communication during such incidents is crucial for maintaining trust and mitigating potential damages.
- Conclusion:
Data privacy in cyber security is a critical aspect of our data privacy in cyber security. Protecting personal and confidential information from cyber threats and data breaches is of utmost importance for individuals and organizations. By understanding the significance of data privacy, addressing key challenges, and implementing strategies such as privacy by design, encryption and anonymization, secure data storage and transmission, employee education, and continuous monitoring, we can strengthen data privacy in the realm of cybersecurity. With a collective effort to prioritize data privacy, we can create a safer and more secure digital landscape where individuals have confidence in the protection of their information.
Conclusion: So above is the Data Privacy in Cybersecurity: Protecting Your Information article. Hopefully with this article you can help you in life, always follow and read our good articles on the website: qule.info
Related Articles
Check Also
Close